|
Research Ideas and Outcomes : Single-media Publication
|
|
Corresponding author: Dasapta Erwin Irawan (dasaptaerwin@outlook.co.id)
Received: 12 Jul 2016 | Published: 18 Jul 2016
© 2016 Dasapta Erwin Irawan, Adhi Priyambodho, Cut Novianti Rachmi, Dimas Maulana Wibowo, Andita Kaesar Fahmi.
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY 4.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Citation: Irawan D, Priyambodho A, Rachmi C, Wibowo D, Fahmi A (2016) Bibliometric study to assist research topic selection: a case from research design on Jakarta’s groundwater (part 1). Research Ideas and Outcomes 2: e9841. doi: 10.3897/rio.2.e9841
|

|
Abstract
This paper is an example to visualize bibliometric data to extract paper’s topics and their citation relation. It is very important to evaluate the number of documents, the intensity of the paper’s topic, and the relationship between papers. The output can be used to pinpoint suitable research topic.
We began with 246 papers, gathered from Google Scholar, Crossref, and Scopus database. We narrowed them down to 70 papers based on language, relevance, pdf availability, and metadata completeness. Open source tools, Vosviewer, Zotero-PaperMachine plugin, were used to visualize the existing reference database.
The following paper gives an illustration that a brief bibliometric analysis could assist a researcher to determine our research path. It gives us a glimpse of research landscape in Jakarta area. Therefore for deeper analysis, we will focus our literature review on groundwater and surface water interactions.
Keywords
Bibliometric, literature review, groundwater, Jakarta
Introduction
Floods have been the main issue in Jakarta every year. Heavy flood occurred in 1996, 2002 and 2007, inundating up to 40% of the city (
Methods
The following bibliometric method was based on several papers on bibliometric (
Data resources
Dataset is available on Figshare (
Results and discussion
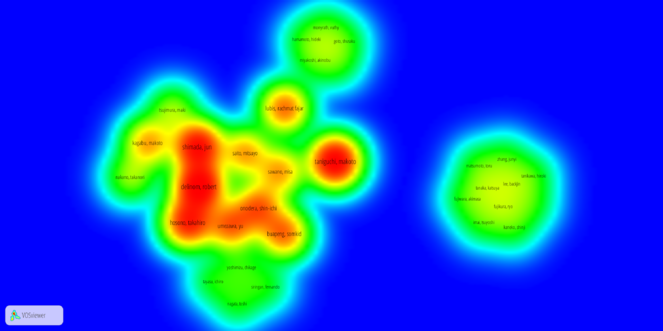
The first result is 47 clusters of paper sorted by keywords, produced by Vosviewer. Only five clusters are connected (
Density map of the papers based on the key words (Red: dense paper population, green: less dense). Dataset is available as
Word cloud analysis in the 1987-2003 show no significant words related to groundwater, while word cloud in 2004-2005 papers starts to show words like "population growth" and "land use". Then in 2005-2006, we could see more mapping-related terms (local/large scale) and quality terms (water contamination and domestic waste), also socio economic terms (richness and indicator). Papers in 2006-2007 mention words like urban development, environment and contamination which reflect the awareness to environmental sustainability. Then in 2007-2008 terms like ecosystem and infrastructure were used. In the following years, technical water-related words like floods, water quality, urbanization, land subsidence, interferometry, and aquifer/groundwater restoration were exposed. Figures are available in
Conclusions
Visualization of bibliometric data could help researchers to pinpoint research path. In this case, the analysis presents a glimpse of groundwater research in Jakarta. We believe more researches should be directed to groundwater-surface water interactions.
Acknowledgements
We thank ITB for giving partial funding and Applied Geology Research Group for valuable comments.
Funding program
This research is partially funded by 2016 Bandung Institute of Technology (BIT) Research Grant.
Grant title
Assessment of Jakarta's water resources.
Hosting institution
Bandung Institute of Technology, Indonesia
Author contributions
- DEI: idea, drafting
- AP: search keys
- CNR: drafting
- DMW and AKF: reference search
Conflicts of interest
The authors state no competing interest upon the publication of this work.
References
-
Jakarta Flood Hazard Mapping Framework. http://www.hkv.nl/upload/publication/Jakarta_Flood_Hazard_Mapping_Framework_MH.pdf. Accession date: 2016 5 04.
-
The contribution of human activities to subsurface environment degradation in Greater Jakarta Area, Indonesia.Science of The Total Environment407(9):3129‑3141. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.10.003
-
Scientific research impact and data mining applications in hydrogeology.The Ohio State University,Ohio,136pp. [InEnglish]. URL: http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1048351
-
PaperMachines: Zotero plug-in for text mining and visualisation.PaperMachines. URL: http://papermachines.org
-
Literature visualisation: Bibliometric of groundwater research in Jakarta.Figshare1(2):1. [InEnglish]. DOI: 10.6084/M9.FIGSHARE.3405685
-
Bibliometrics: an overview. https://library.leeds.ac.uk/downloads/file/265/bibliometrics_an_overview. Accession date: 2016 5 01.
-
Groundwater recharge and discharge processes in the Jakarta groundwater basin, Indonesia.Hydrogeology Journal16(5):927‑938. DOI: 10.1007/s10040-008-0278-1
-
Twenty years of global groundwater research: A Science Citation Index Expanded-based bibliometric survey (1993–2012).Journal of Hydrology519:1. [InEnglish]. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.07.064
-
Citation data analysis on hydrogeology.Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology58(4):1. [InEnglish]. DOI: 10.1002/asi.20526
-
Hydrogeological Research: Beginning of the End or End of the Beginning?Ground Water39(4):492‑498. DOI: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.2001.tb02337.x
-
WHITEPAPER USING BIBLIOMETRICS: A guide to evaluating research performance with citation data. http://ip-science.thomsonreuters.com/m/pdfs/325133_thomson.pdf. Accession date: 2016 5 04.
-
Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping.Scientometrics84(2):523‑538. DOI: 10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3
-
VOSviewer manual.Leiden: Univeristeit Leiden1:1. URL: www.vosviewer.com/documentation/Manual_VOSviewer_1.5.4.pdf
-
Text mining and visualization using VOSviewer.arXiv preprint arXiv:1109.20581:1. URL: http://arxiv.org/abs/1109.2058
-
RIS (file format). https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RIS_(file_format). Accession date: 2016 7 06.
-
Thirty years (1984-2014) of groundwater science teaching and research in China: A dissertation-based bibliometric survey.Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering3(3):1. URL: http://gwse.iheg.org.cn/EN/abstract/abstract190.shtml
-
Visualizing readership activity of Mendeley users using Vosviewer.Figshare1:1. [InEnglish]. DOI: 10.6084/M9.FIGSHARE.1092521.V1
-
Methods for Bibliometric Analysis of Research: Renewable Energy Case Study. http://web.mit.edu/smadnick/www/wp/2009-10.pdf. Accession date: 2016 5 04.
-
Zotero: An open source reference manager.Zotero Community. URL: http://zotero.org
Supplementary materials
This file stored the list of 70 papers discussed in the article.
Download file (5.59 kb)
This pdf consists of word cloud (1987-2015) images discussed in the paper
Download file (320.96 kb)