|
Research Ideas and Outcomes : Research Presentation
|
|
Corresponding author: Robert Jeenchen Chen (rjcc@ntu.edu.tw), Chwan-Chuen King (chwanchuen@gmail.com)
Received: 22 Jun 2016 | Published: 29 Jun 2016
© 2016 Robert Jeenchen Chen, Cheng-Chung Fang, Fuh-Yuan Shih, Chwan-Chuen King.
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY 4.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Citation: Chen R, Fang C, Shih F, King C (2016) A Scoring System for Identifying Severe Cases of Influenza-like Illness by Comorbidity and Age - A Nationwide Cohort Analysis. Research Ideas and Outcomes 2: e9648. doi: 10.3897/rio.2.e9648
|

|
Abstract
Background
Identification of high-risk severe cases from influenza-like illness (ILI) is crucial for disease surveilance and clinical management. Comorbidity and demography profile may be a good risk estimation. The study utilized Taiwanese National Health Insurance Database, ICD-9, and Marsden-Haug’s ILI Codes to measure the effect of systemic classes of comorbidity on four outcomes: ospitalization cost, length of stay (LOS), death, and intensive care unit (ICU) entry.
New information
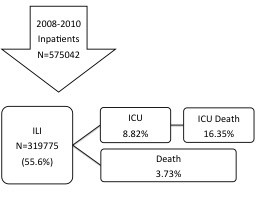
From 2008 to 2010, there were 319,775 ILI inpatient cases, of which 8.82% entered ICU and 3.83% died at hospital discharge. The significant comorbidity attributes varied in each age stratum: heart failure in any age, non-dialyzed renal insufficiency in any age, cancer in school-age children up to mid-age adults, tuberculosis in the elderly, stroke in adults, congenital anomaly in children and adolescents, transplant in school-age up to adolescents, or HIV in young adults.
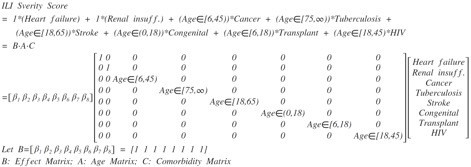
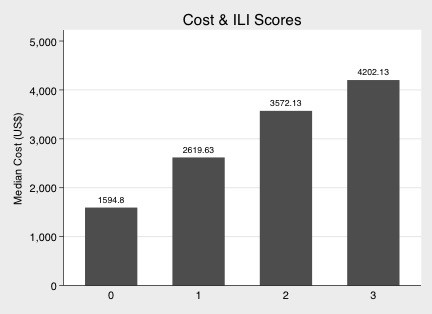
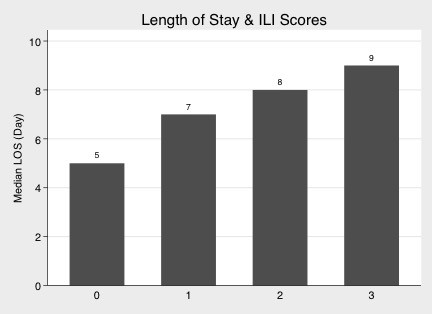
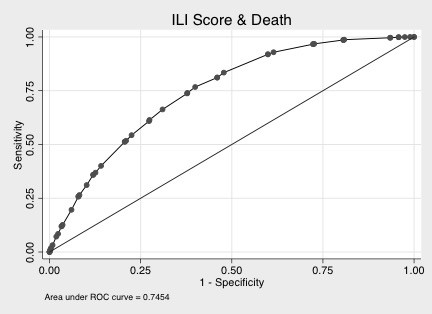
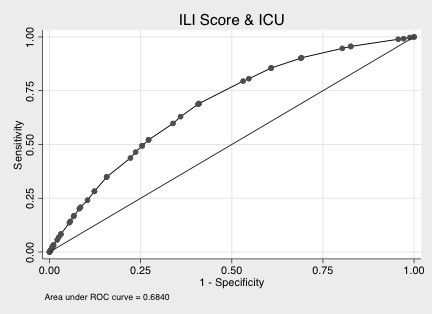
Comorbidity vector was (heart failure, non-dialyzed renal insufficiency, cancer, tuberculosis, stroke, congenital anomaly, transplant, HIV). Age vector was (1, 1, 6<=age<45, 75<=age, 18<=age<65, 0<age<=18, 6<=age<18, 18<=age<45). Comorbidity score, the dot product of comorbidity vector and age vector, showed significant correlation with hospitalization cost (Spearman rho=0.1885, p<0.0001), and with LOS (Spearman rho=0.1717, p<0.0001). Its ROC area-under-curves (AUC) were 0.7454 with death and 0.6840 with ICU.
The risk estimation model could facilitate us to address population measures for upcoming severe influenza epidemics, and further allocate resources optimally.
Keywords
Influenza-like illness; comorbidity; ICD-9; risk model
Introduction
Influenza-like illness (ILI) is often the initial presentation of influenza for practicing clinicians. With limited healthcare resources and medical attention, it becomes paramount to identify high-risk ILI cases by their comorbidity attributes for appropriate case management.
Presentation
The research was presented in:
Options for the Control of Influenza VIII, Cape Town, South Africa, 5-9 September 2013
Clinical Management Poster Session (
Methods
Retrieved from the one-million-per-year systematic samples of Taiwanese National Health Insurance Databases from 2008 to 2010, our cohort composed of all inpatient encounters (admissions) with the diagnostic ICD-9 (International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision) that matched the ILI definition proposed by Marsden-Haug’s Code-based Syndromic Surveillance (
Univariate and multivariate analyses were done with the dependent variables as worse outcome, and the comorbidity attributes as covariates with the adjustment for gender in pre-defined age strata. The selected comorbidity attributes formulated Comorbidity vector and the corresponding age strata formulated Age vector. Comorbidity score was defined as the dot product of Comorbidity vector and Age vector. Its performance was assessed by Spearman correlation and by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves.
Data resources
Data used to produce figures are deposited in the Taiwanese National Healtn Insurance Research Database
Selected raw datasets, SAS/SQL programs, and Stata programs are available on the following weblink:
https://www.dropbox.com/sh/lzm4z3zt3imcpwa/AABrFngHGJ5KLHAIAhtCpE7Ga?dl=0
One of the processed datasets for Stata 14 is published with the present paper as an example (
Results and discussion
From 2009 to 2010, our cohort had 319,775 ILI inpatient cases, of which 8.82% entered ICU and 3.83% died at hospital discharge (
Comorbidity vector was (heart failure, non-dialyzed renal insufficiency, cancer, tuberculosis, stroke, congenital anomaly, transplant, HIV). Age vector was (1, 1, 6<=age<45, 75<=age, 18<=age<65, 0<age<=18, 6<=age<18, 18<=age<45) (
Higher clinical alertness should be set once an ILI case matches the following age-specific comorbidity attributes: heart failure in any age, non-dialyzed renal insufficiency in any age, cancer in school-age children up to mid-age adults, tuberculosis in the elderly, stroke in adults, congenital anomaly in children and adolescents, transplant in school-age up to adolescents, or HIV in young adults.
With the ILI severity score calculated, the score-plus-1 effects were significant on all outcomes of the study (
Effect of ILI score +1 (adjusted for age and sex) on outcomes
|
Outcomes |
Statistics |
Effect |
95% CI |
p |
|
|
Cost |
Ratio |
1.44 |
1.42 |
1.45 |
<0.0001 |
|
LOS |
Ratio |
1.26 |
1.25 |
1.27 |
<0.0001 |
|
Death |
OR |
1.21 |
1.19 |
1.23 |
<0.0001 |
|
ICU |
OR |
1.87 |
1.84 |
1.91 |
<0.0001 |
|
AE |
OR |
1.42 |
1.40 |
1.44 |
<0.0001 |
Conclusions
The risk estimation model could facilitate us to address population measures for upcoming severe influenza epidemics, and further allocate resources optimally for prevention and control in public health decision-making.
Presented at
Options for the Control of Influenza VIII, Cape Town, South Africa, 5-9 September 2013. See original poster (
Acknowledgements
Special thanks for Ms. Wen-Wen Wang for her administrative supports.
Grant title
Taiwanese National Health Insurance Database Research.
Hosting institution
National Taiwan University College of Public Health, Taipei, Taiwan
Ethics and security
Waived IRB review.
Author contributions
Chen RJC: study design, manuscript writing, data management, and statistical analysis; Fang CC: concept proposal and research advice; Shih FY: study design and research advice; King CC: study design and supervision.
References
-
Code-based syndromic surveillance for influenzalike illness by International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision.Emerging infectious diseases13(2):207‑216. [InEnglish]. DOI: 10.3201/eid1302.060557
Supplementary materials
Options for the Control of Influenza VIII Conference Programme Book
Download file (7.21 MB)
A sample SAS SQL program code fragment is attached.
The more complete version is available upon request.
Download file (10.57 kb)
A sample Stata program code fragment is attached.
The more complete version is available upon request.
Download file (4.83 kb)
The poster presented in the Conference.
Download file (684.03 kb)
The dataset used for in Stata 14 format. The other datasets are available upon request.
Download file (56.21 MB)