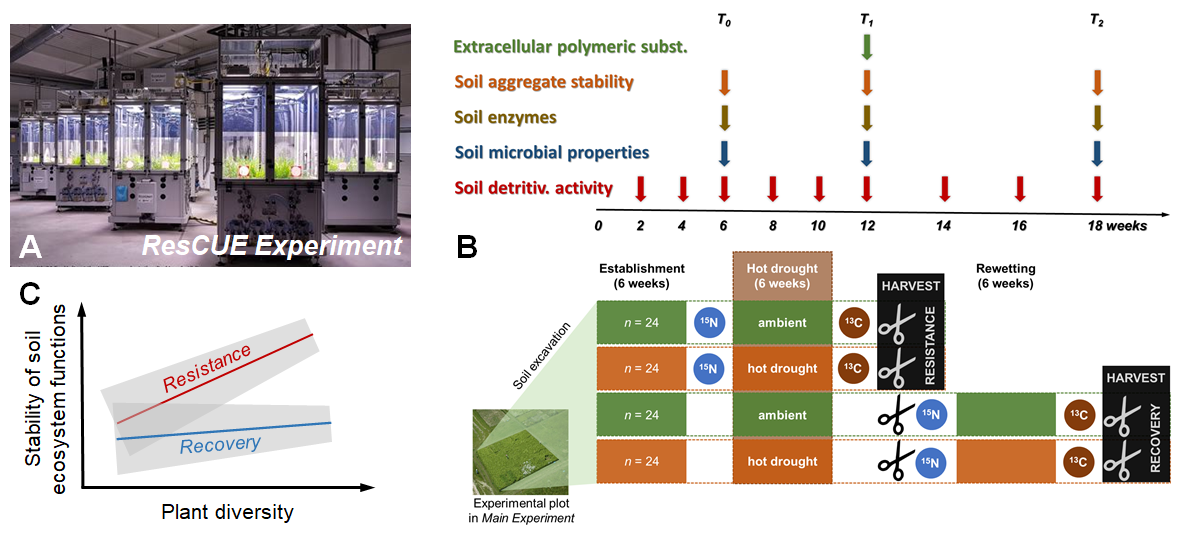
Figure depicting the data sources, analyses and hypotheses of Work Package (WP) 3: A: Experimental units used for the ResCUE Experiment in the iDiv Ecotron. B: The main sampling campaigns of the ResCUE Experiment. We will measure different biological, chemical and physical soil processes repeatedly over the course of the experiment. While soil detritivore feeding activity will be measured every two weeks (8 campaigns x n = 96 lysimeters), soil microbial properties, soil extracellular enzymes and soil aggregate stability will be measured three times (right before the experimental drought [Time0 = T0; n = 96]; right after the drought [T1; n = 96]; and after 6 weeks of recovery [T2; n = 48]) and exopolysaccharides will be measured once (T1; n = 96). C: Illustration of the hypothesis that plant diversity increases the temporal stability, as well as resistance to and recovery after a hot drought, of multiple soil properties and multistability.