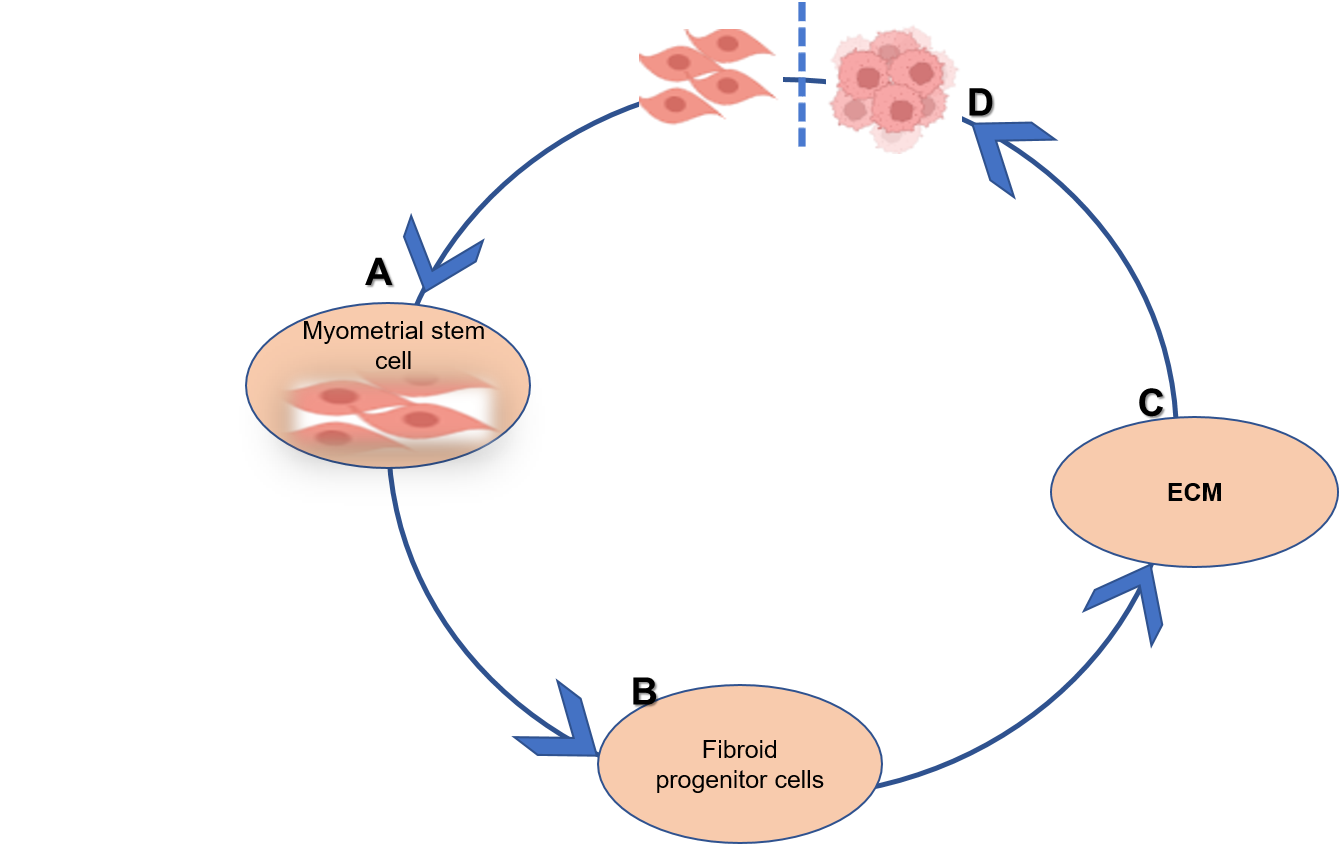
Illustration of UF disease formation, A is transformed into a progenitor cell when influenced by environmental and genetic factors. B differentiates into four primary cell types: fibroblast, fibroid-associated fibroblast, smooth muscle cells and vascular smooth muscle cells which then produce C extracellular matrix (ECM) of the fibroids. Further influence of environmental and molecular factors promote the growth and proliferation of these cells and consequently, the clinically relevant fibroids (D).